What is it for?
- The Product Backlog should constantly reflect the work in progress as well as future features, even if not all of them will be implemented at the end of the project.
- It’s important to note that not all items in the Product Backlog require the same level of detail. It can contain ready-to-develop User Stories , but also features, technical tasks, and possibly bugs.
- The goal of Product Backlog Review (Product Backlog Refinement or Grooming in Scrum) is to enrich the Product Backlog items by adding details, estimates, and priorities.
Attention !
To simplify our rituals, we confuse Backlog Review, Refinement, and Grooming, although some agilists distinguish between them
When to Do a Product Backlog Review?
Product Backlog Review is a meeting that occurs once or twice during each Sprint, usually in the middle of the Sprint rather than at the beginning. It lasts about 2 hours.
During this meeting, the main input element is the Product Backlog that has been prioritized. The purpose of the meeting is to review the Product Backlog and update it as needed.
At the end of the Product Backlog Review, the result is a refined and improved Product Backlog.
This means that the team has a clearer understanding of the items in the Product Backlog, making it easier to plan during sprint planning for the upcoming Sprint.
The Sprint Backlog, on the other hand, is created during Sprint Planning.
Frequency
Once or twice per Sprint rather in the middle of the Sprint than at the beginning
1
Duration
About 2 hours.
2
Inputs
Prioritized Product Backlog
3
Outputs
Product Backlog reviewed and fixed
4
Frequency
Once or twice per Sprint rather in the middle of the Sprint than at the beginning
1
Duration
About 2 hours.
2
Inputs
Product Backlog prioritized.
3
Outputs
Sprint Backlog reviewed.
4
Who Participates in Product Review?
The Product Backlog Review is a collaborative work between the Product Owner, the Dev Team and the Business Analyst.
The following people are participating in the review:
- Scrum Team: Product Owner, Scrum Master, Dev Team (full or not)
- If applicable: Tech Lead, Business Analyst, Quality Analyst.
- Anyone who can add value to these meetings.
How do you run a Product Backlog Review?
Points to Address During the Review
The Product Backlog Review with the Product Owner focuses on the following aspects. Each of these points will be discussed in more detail.
Vision
- Work on the vision for review and update
Product Backlog
- Work on the Product Backlog items:
- The New
- The Abandoned
- The existing ones
Release
- Work on the Release Plan
Sticking Points
- List with associated items (which are therefore in a state of technical and/or functional blockage)
Note: In an agile process, anomalies and fixes are considered Product Backlog entries.
Work on the Vision
This is to check if the Product Vision has changed:
- Review of the current vision.
- Identification of factors that change the vision.
- Updated vision in relation to these changes.
- Identification of impacts on the Release Plan
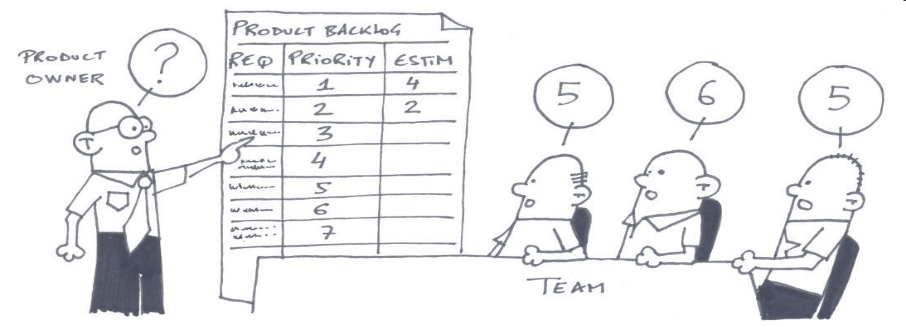
Work on Product Backlog Items
All the elements of the Product Backlog (User Stories, Technical Tasks, Bugs…) can be addressed during this review.
Existing elements:
- Verification of the team’s understanding of the need
- Possibly re-evaluation if necessary
- Add/Remove an item from the Product Backlog based on the re-evaluation (add if downgraded, delete if upscaled)
Discontinued items:
- Explanation of the reasons for abandonment.
- Analysis of the impact of this abandonment on the scope of the project, including potential changes.
- Replacement with an element of the same complexity if applicable.
The new elements:
- Verification of the team’s understanding of the need
- Estimating Items in Story Points
- Planning for a future Sprint if possible
- Removal of an element of equivalent complexity if applicable
Preparation for the next Sprint:
- Presentation of the projected objective of the Sprint.
- List of forecasting elements for the next Sprint
- Verification of compliance with the definition of Ready.
- Ensure the proper granularity of the elements of the upcoming Sprint.
Work on the Release Plan and Sticking Points
The distribution of elements in sprints:
- Review of the distribution of elements: after the review of the Product Vision, a reestimation, an addition or deletion of an element, the forecast scope of the upcoming Sprints must be reviewed.
Blocked items:
- Identification of blocking reasons (technical, architectural, organizational, etc.)
- Definition of an action plan: development of a POC (Proof Of Concept), intervention of an expert
Recommendations
Spritn Review
- Avoid scheduling the review during the 20% start or end of the Sprint.
Complexity
- When the project is complex (e.g. several teams in parallel), don’t hesitate to do informal reviews or workshops before the review.
- In any case, the Product Owner should set up internal workshops on the customer side, to refine his understanding of the need.
Prioritization
- Make sure everyone understands that the prioritizations and estimates made during the Product Backlog Review are not final: they will only be finalized during the Sprint Planning.
Control
- The Product Owner must be proficient in the elements of the Product Backlog that he is going to present, he must know the details. Similarly, review participants can review the Product Backlog the day before.
Granularity
- Don’t hesitate to cut out an element during the review, that’s what it’s for!
Anticipation
- Make sure that the Product Owner is well aware that with each review of the Product Backlog, it should have enough elements so that there is work for both Sprints according to the Sprint in progress.
- Don’t focus the Product Backlog review only on the N+1 Sprint
- Allow yourself to look at things that should be dealt with much later.
Aftercare
- Whenever there is a significant risk or dispute on an item in the Product Backlog, don’t try to resolve it in session, but create an action and follow it.
Advise
- Don’t forget the team’s advisory role to the Product Owner whether on methodological, technical or functional aspects.
- On an integration project, for example, the Technical Expert and the Business Analyst must try to ensure compliance with the out of the box solutions.

Complement
Read also:








0 Comments